Dr. Gulgun Sengul is one of the creators of the first and the only atlases of the spinal cord of humans, and research animals (monkey, mouse and rat). These atlases are used for identification of the spinal cord structures in experimental animal research studies and postmortem human studies by physicians and researchers working on spinal cord diseases such as spinal cord injury, spinal muscular atrophy and ALS, or animal models of these diseases.
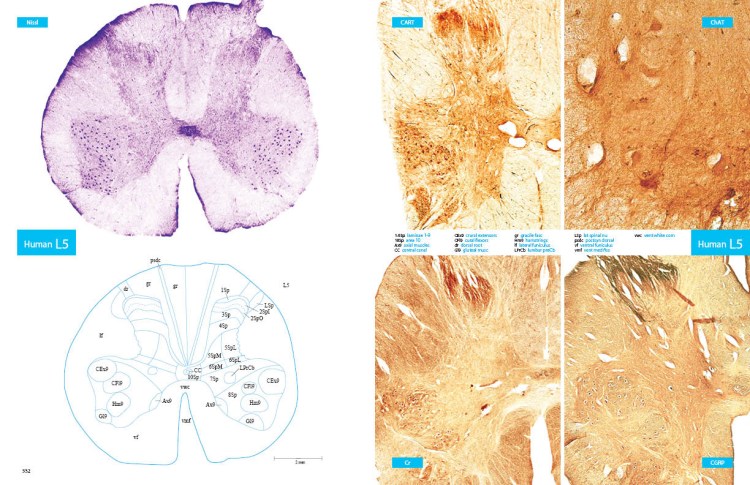
The spinal cord maps (atlases) Dr. Sengul created are assisting all spinal cord researchers in studying disease, interpreting research imaging data, and improving the accuracy of therapeutic interventions on the spinal cord in neurosurgery. These atlases have been widely used and highly cited in international books and research articles up to date.
Dr. Sengul’s extensive investigations in the field identified the location of all ten layers and thirteen nuclei (neuronal cell groups with a specific function) of the human spinal cord for the first time in the literature. These ten layers and nuclei are responsible for receiving sensations from the body and transmitting commands from the brain to the body.

Sengul G. Atlas of the human spinal cord. In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Watson C, Tanaka I, Paxinos G, Atlas of the spinal cord: mouse, rat, rhesus, marmoset, and human. Academic Press Elsevier, London, 2013.
Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G. Atlas of the rat spinal cord. In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Watson C, Tanaka I, Paxinos G, Atlas of the spinal cord: mouse, rat, rhesus, marmoset, and human. Academic Press Elsevier, London, 2013.
Watson C, Paxinos G, Kayalioglu G, Heise C. Atlas of the rat spinal cord. In: The Spinal Cord. A Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation Text and Atlas. Watson C, Paxinos G, Kayalioglu G (eds). Academic Press Elsevier, 2009.
Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G. Atlas of the mouse spinal cord.In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Watson C, Tanaka I, Paxinos G, Atlas of the spinal cord: mouse, rat, rhesus, marmoset, and human. Academic Press Elsevier, London, 2013.
Watson C, Paxinos G, Kayalioglu G, Heise C. Atlas of the mouse spinal cord. In: The Spinal Cord. A Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation Text and Atlas. Watson C, Paxinos G, Kayalioglu G (eds). Academic Press Elsevier, 2009.
Sengul G, Puchalski R, Watson C. Atlas of the newborn mouse spinal cord. In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Puchalski RB, Watson C. Cytoarchitecture of the spinal cord of the postnatal (p4) mouse. Anatomical Record 295:837-845, 2012.
Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G. Atlas of the rhesus monkey spinal cord.In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Watson C, Tanaka I, Paxinos G, Atlas of the spinal cord: mouse, rat, rhesus, marmoset, and human. Academic Press Elsevier, London, 2013.
Watson C, Sengul G, Tanaka I, Rusznak Z, Tokuno H. The spinal cord of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Neuroscience Research 93:164-175, 2015.
Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G. Atlas of the marmoset spinal cord. In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.
Sengul G, Watson C, Tanaka I, Paxinos G, Atlas of the spinal cord: mouse, rat, rhesus, marmoset, and human. Academic Press Elsevier, London, 2013.
Robertson B, Sengul G., Wallen P, Grillner S. The cyclostome spinal cord. In: The Mammalian Spinal Cord, Watson C, Sengul G, Paxinos G, Academic Press Elsevier, 2022.